Recently, SBI bank advised its customers to use the bank’s own ATM network after the security breach of around six lakh debit cards issued by the bank. Further, reports say that around 32 lakhs debit cards belonging to major banks have been compromised in India. Cyber crimes are increasing in India elsewhere, it is time too look at India’s cyber security infrastructure and cyber security agencies.
What is Cyberspace?
Cyberspace is a complex environment consisting of interactions between people, software and services, supported by worldwide distribution of information and communication technology devices and networks (internet).
Why is Cyber Security critical?
After China and the U.S., India has the highest number of Internet users. The number of Internet users in India increased from 1.4 million in 1998 to 500 million, as of today. There are also an estimated over 371 million mobile phone subscriptions with Internet connectivity. These users are at constant threat of any cyber crime.

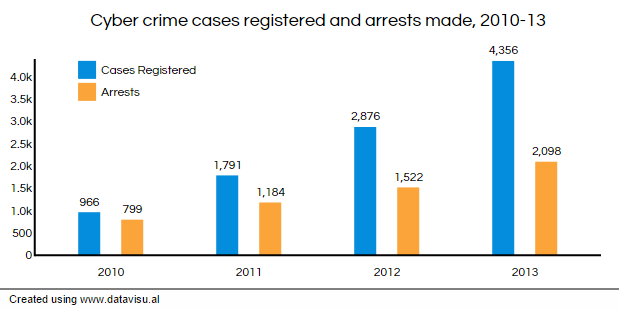
According to statistics from the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), In the three years up to 2013, registered cases of cyber crime were up 350%, from 966 to 4,356.
Further, India’s infrastructure is susceptible to four kinds of digital intrusions:
- Espionage, which involves intruding into systems to steal information of strategic or commercial value;
- Cybercrime, referring to electronic fraud or other acts of serious criminal consequence;
- Attacks, intended at disrupting services or systems for a temporary period; and
- War, caused by a large-scale and systematic digital assault on India’s critical installations.
India’s Cyber Security Policy:
India released a National Cyber Security Policy in 2013, summarized as below
Vision
- To build a secure and resilient cyberspace for citizens, businesses and Government
Mission
- To protect information and information infrastructure in cyberspace, build capabilities to prevent and respond to cyber threats, reduce vulnerabilities and minimize damage from cyber incidents through a combination of institutional structures, people, processes, technology and cooperation
Objectives
- To create a secure cyber ecosystem in the country, developing effective public-private partnerships and collaborative engagements through technical and operational cooperation.
- Enabling goals aimed at reducing national vulnerability to cyber attacks, preventing cyber attacks & cyber crimes, minimizing response & recover time and effective cyber crime investigation and prosecution.
Strategy:
- Create a National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC), which will act as a 24×7 centre to battle cyber security threats in strategic areas such as air control, nuclear and space. It was created on January 16, 2014, and placed under the technical intelligence agency, the National Technical Research Organization.
- The current agency, Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT), will deal with all public and private infrastructure
- Create a workforce of around 500,000 trained in cyber security.
- Provide fiscal benefits to businesses to adopt best security practices.
- Set up testing labs to regularly check the safety of equipment being used in the country.
- Building indigenous security technologies through research.
India’ Cyber Security Infrastructure:
Recognizing the strategic dimensions of cyberspace, the Prime Minister’s Office (PMO) created the position of the National Cyber Security Coordinator in 2014. There is also a Joint Working Group (JWG) on Cyber Security led by the National Security Advisor.
However, India also has multiple agencies looking into different dimensions of cyber space and cyber crimes.
The National Technical Research Organization (NTRO)
- Set up in 2004, it is a technical intelligence agency under the National Security Adviser in the Prime Minister’s Office, India.
- It also includes National Institute of Cryptology Research and Development (NICRD).
- NTRO also oversees functioning of National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC)
National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC)
- It is the National Nodal Agency to protect National Critical information infrastructure (NCII).
- Identify such critical infrastructure (defined at end of article).
- Initiate counter-measures in cooperation with other security agencies and private corporate entities that man these critical sectors.
Indian-Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In)
- Established in 2004, CERT-In function under Department of Electronics and Information Technology (DEITy)
- CERT-In is India’s response to cyber threats and has following charter, mission and constituency.
- Charter: “The purpose of the CERT-In is, to become the nation’s most trusted referral agency of the Indian Community for responding to computer security incidents as and when they occur”.
- Mission “To enhance the security of India’s Communications and Information Infrastructure through proactive action and effective collaboration.”
- Constituency: The CERT-In’s constituency is the Indian Cyber-community.
- CERT-In is mandated under the IT Amendment Act, 2008 to serve as the national agency in charge of cyber security.
- Since Nov 2012, DG of CERT-In is called the National Cyber Security Coordinator (NCSC)
Cyber Crime Cell – Central Bureau of Investigation ( CBI):
- CBI has the following specialized structure for cyber crimes:─
- Cyber Crimes Research and Development Unit (CCRDU);
- Cyber Crime Investigation Cell (CCIC);
- Cyber Forensics Laboratory; and
- Network Monitoring Centre.
State Police- Cyber Crime Cells
- Out of the 29 States and seven UTs, 19 States and two UTs possess Cyber Crime Cells.
Proposed:
National Cyber Coordination Centre is a proposed cyber security and e-surveillance agency in India. It is intended to screen communication metadata and co-ordinate the intelligence gathering activities of other agencies.
Surveillance programs in India:
Central Monitoring System
The Central Monitoring System, abbreviated to CMS, is a clandestine mass electronic surveillance data mining program installed by the Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT), an Indian Government owned telecommunications technology development centre, and operated by Telecom Enforcement Resource and Monitoring (TERM) Cells.
The CMS gives law enforcement agencies centralized access to India’s telecommunications network and the ability to listen in on and record mobile, landline and satellite calls and voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), and read private emails, SMS and MMS and geolocate people via their cell phones, all in real time.
NATGRID
NATGRID is an intelligence sharing network that collates data from the standalone databases of the various agencies and ministries of the Indian government.
It is a counter terrorism measure that collects and collates a host of information from government databases including tax and bank account details, credit card transactions, visa and immigration records and itineraries of rail and air travel.
This combined data will be made available to 11 central agencies including the R&AW, the National Investigation Agency, the CBI, the Directorate of Revenue Intelligence, the Intelligence Bureau, the Narcotics Control Bureau and the Enforcement Directorate.
DRDO NETRA
NETRA (NEtwork TRaffic Analysis) is a software network developed by India’s Centre for Artificial Intelligence and Robotics (CAIR), a Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) laboratory, and is used by the Intelligence Bureau, India’s domestic intelligence agency, and the Research and Analysis Wing (RAW), the country’s external intelligence agency to intercept and analyze internet traffic using pre-defined filters.
Lawful Intercept and Monitoring (LIM) systems
Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT) deployed the LIM systems for the monitoring of Internet traffic, emails, web browsing, Skype and any other Internet activity of users in India.
CCTNS
Crime and Criminal Tracking Network & Systems (CCTNS) is a Mission Mode Project (MMP) under the National e-Governance Plan of Govt. of India.
It facilitates the collection, storage, retrieval, analysis, transfer and sharing of data and information at the police stations and between the police stations and the State Headquarters and the Central Police Organizations.
Terms:
Critical infrastructure:

